Same-day treatments are available.
The Connection Between Diet and Your Child’s Dental Health
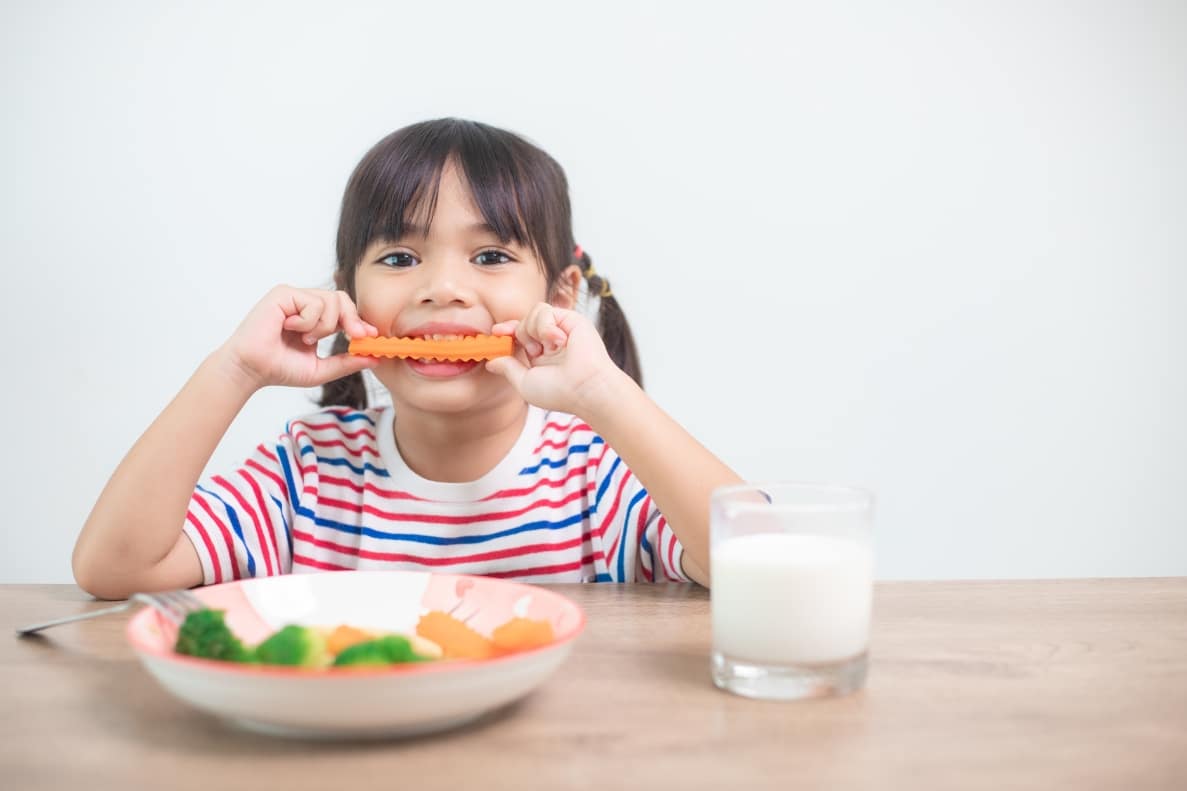

A healthy smile begins with a balanced diet. What your child eats plays a critical role in their dental health. Poor nutrition can lead to cavities, gum disease, and weak enamel, while nutritious foods can strengthen teeth and support oral hygiene. Many parents overlook the relationship between diet and dental care, but understanding this connection can help prevent common oral health problems. This blog dives into how food choices impact your child’s dental health and offers actionable tips to keep their smile bright and healthy.
How Sugar Impacts Your Child’s Teeth?
Excess sugar is a leading cause of cavities in children—bacteria in the mouth feed on sugar, producing acids that weaken enamel and cause tooth decay.
- Common sources of sugar: candy, sodas, juices, and processed snacks.
- Hidden sugars in “healthy” snacks: granola bars, flavored yogurts, and fruit juices.
- Encourage alternatives like fresh fruits or unsweetened snacks to reduce sugar intake.
The Role of Calcium and Vitamin D in Strong Teeth
Calcium and vitamin D are essential for developing strong teeth and bones. A deficiency can lead to weaker enamel and higher cavity risks.
- Include dairy products like milk, cheese, and yogurt in your child’s diet.
- Non-dairy options: fortified plant-based milk, leafy greens, and almonds.
- Sunlight exposure helps the body produce vitamin D naturally.
Foods That Protect Against Cavities
Some foods actively help protect your child’s teeth from cavities. They neutralize harmful acids and provide essential nutrients for oral health.
- Pediatric dentists recommend crunchy fruits and vegetables like apples and carrots to increase saliva flow, which washes away bacteria.
- Nuts and seeds contain healthy fats that coat teeth, acting as a natural shield.
- Cheese and yogurt neutralize acids and strengthen enamel.
Harmful Eating Habits to Avoid
Diet isn’t just about what kids eat but how and when they eat. Certain habits can contribute to poor oral health.
- Frequent snacking increases the risk of decay because it doesn’t allow saliva to neutralize acids.
- Sticky snacks like gummies and dried fruits cling to teeth, promoting bacterial growth.
- Drinking sugary beverages before bed allows sugars to linger in the mouth overnight.
Hydration and Its Importance for Oral Health
Water is often underestimated but plays a crucial role in maintaining oral hygiene.
- Fluoridated water strengthens enamel and prevents cavities.
- Drinking water after meals washes away food particles and bacteria.
- Avoid sugary drinks and encourage plain water as the primary beverage for hydration.
Building a Child-Friendly, Teeth-Friendly Diet
Creating a diet that promotes oral health doesn’t have to be complicated. Incorporate foods that naturally clean teeth and strengthen gums.
- Breakfast ideas: whole-grain toast with avocado, scrambled eggs, or fruit smoothies without added sugar.
- Lunchbox suggestions: cheese cubes, sliced vegetables, whole fruits, and nuts.
- Fun snacks: frozen banana slices, plain popcorn, or yogurt with fresh berries.
Educating Kids About the Diet-Dental Health Connection
Teaching your child how food affects their teeth helps build lifelong healthy habits.
- Use visual aids like diagrams showing how sugar causes cavities.
- Create a reward system for choosing teeth-friendly snacks.
- Involve kids in meal prep to encourage them to try healthy options.
Your child’s diet is a cornerstone of their dental health. Choosing the right foods and avoiding harmful habits can lay the foundation for a strong, healthy teeth lifetime. Small changes, like reducing sugary snacks or including calcium-rich foods, can significantly affect oral hygiene. Want personalized advice for your child’s dental care? Schedule a consultation with our pediatric dental team today and set your child up for a healthier smile.

7 Foods and Drinks to Avoid After Professional Teeth Whitening in Cypress
What to Expect After a Root Canal Treatment in Cypress



